Quality Management Services
Audit Quality Advisory Services for Accounting Firms
Quality Management Services
Quality management is a critical component for firms of all audit practices, including issuer and broker-dealer audits. Firms are required to comply with quality management and quality control standards related to their system of quality management. Specifically, the IAASB, AICPA, and PCAOB have adopted ISQM 1, SQMS 1, and QC 1000, respectively. As a result, firms that are required to follow IAASB, AICPA or PCAOB standards need to reconsider their quality management systems and implement policies and procedures to comply with these requirements.
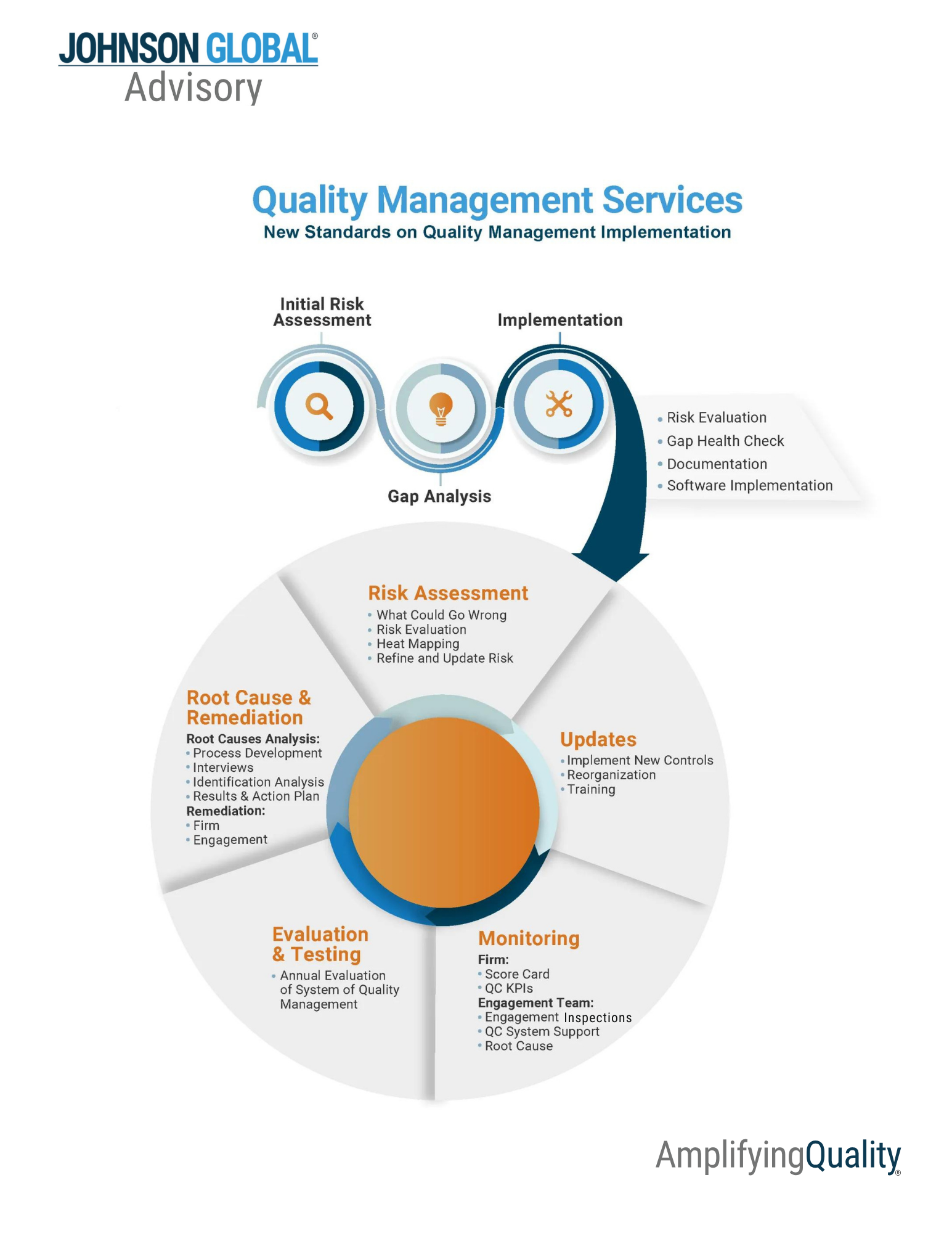
The following diagrams depicts the steps that a firm should undertake to initially adopt and implement the quality management standards and the iterative and cyclical nature of operating their system of quality management on an annual basis:
Through our experiences evaluating systems of quality control at firms that operate domestically and internationally and completing hundreds of firm inspections, we as Advisors, meet firms where they are and understand the significant effort and the changes required by firms to implement and operate their system of quality management under the new quality management framework. These required changes will affect firms around the globe due to the amount of effort involved given the rigor of these standards.
We have supported firms' initiatives to establish the appropriate policies, processes and systems to address the changes required in the adoption of the quality management standards. These changes include developing a robust risk assessment process, establishing governance and leadership controls, expanding firm policies and controls around independence and ethics requirements, and identifying and establishing appropriate policies and controls for firm technological, intellectual, and human resources. This work also includes developing or improving processes and controls over monitoring and remediation, including root cause analyses.
JGA has the experience and the team to help firms implement and operate their system of quality management and comply with the quality management standards.

Our Services Include:
Risk Assessment
- Identify the “what could go wrongs”
- Perform a risk evaluation
- Assist or perform risk heat mapping development and implementation
- Refine and update risks
Implementation and Training
- Assist with new or revised control implementation
- Support reorganization/realignment
- Develop, deliver, and consult on training programs
Monitoring
- At firm level
- Develop and implement score cards and QC KPIs
- At engagement level
- Perform pre- and post-inspections
- Perform root cause analysis, including
- interviews with engagement teams
Evaluation and Testing
- Assist with the annual evaluation of the system of Quality Management including development, implementation and evaluation
Quality Management Readiness
- Perform an initial risk assessment
- Perform a gap health check on key components of the firm’s QC process
- Support QC documentation efforts
- Advise on software implementation
- Refine and assist with developing QC processes
Root Cause and Remediation
- Root Cause
- Assist with methodology / audit tool development
- Conduct interviews
- Perform and analysis of root cause findings
- Complete and report on root cause analysis
- Remediation
- Design and execute on remedial action plans for firm-level deficiencies
- Assist with engagement level remediation and resolution